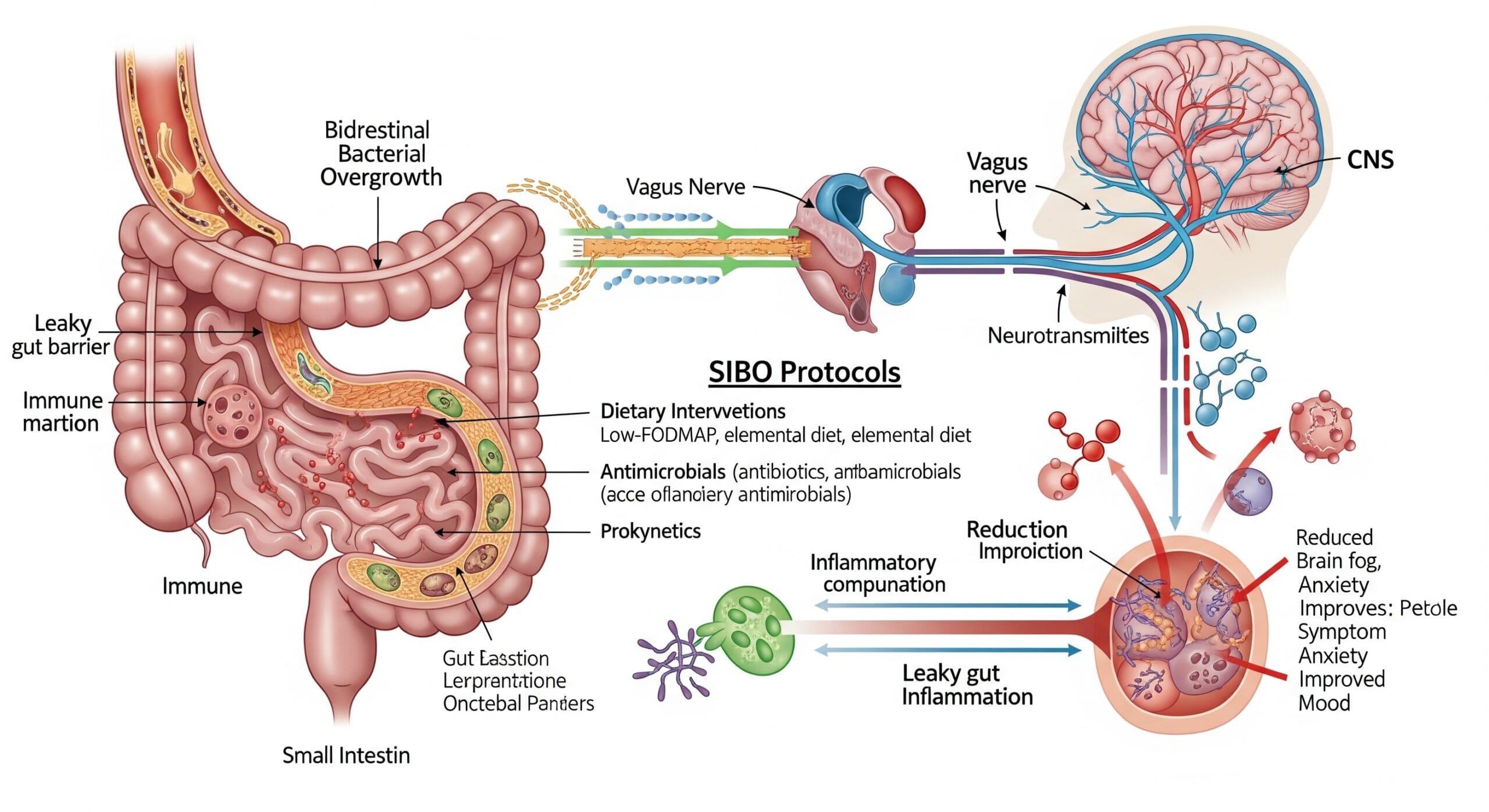
1. Know your genetic susceptibility
Consider what diseases are in your family. By looking at your genetics you can make huge preventative steps so you don’t follow the same path. This doesn’t mean we look at serious genetic diseases like the BRCA gene for breast cancer but rather the metabolic genes that control how you make B12, folate, metabolise fat, make brain chemicals, detox etc.
2. Make a personalised Healthcare Plan:
Work with healthcare professionals to create a personalised healthcare plan based on your genetic susceptibility. This may include lifestyle modifications, supplements and preventive measures tailored to your specific genetic profile to really ‘plug up those potholes’.
3. Lifestyle Modifications:
Discover the lifestyle changes based on your genetic predispositions. For example, if you have a genetic risk for heart disease, you might focus on maintaining a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress.
4. Get regular Health Check-ups:
Schedule regular health check-ups and testing based on your genetic risk factors. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for many conditions.
5. Nutritional Guidance:
Seek guidance from your healthcare practitioner to develop a diet plan that aligns with your genetic predispositions. Some genetic variations may influence how your body responds to certain nutrients, and a personalised nutrition plan can optimise your health.
6. Fitness and Exercise Planning:
Tailor your exercise routine to your genetic makeup. Some individuals may be more predisposed to certain types of exercise-related benefits, such as endurance or strength, based on their genetic profile.
7. Environmental Risk Factors:
Consider environmental factors that may interact with your genetic susceptibility. For example, if you have a genetic predisposition to respiratory conditions, minimising exposure to environmental pollutants becomes crucial.
8. Stay Informed:
Stay updated on new research and developments in the field of genetics and health. As our understanding of genetics advances, new interventions and preventive strategies may emerge.
9. Regular Health Monitoring:
Keep track of your health metrics, and if there are any changes or new symptoms, consult with healthcare professionals promptly.