What is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a sever mental disorder (or group of disorders) characterised by a disintegration of the process of thinking, of contact with reality, and of emotional responsiveness.
Delusions and hallucinations (especially of voices) are usual features, and the individual usually feels that their thoughts are being controlled by, or shared with, others.
Individuals often become very socially withdrawn and they lose energy and motivation.
Research
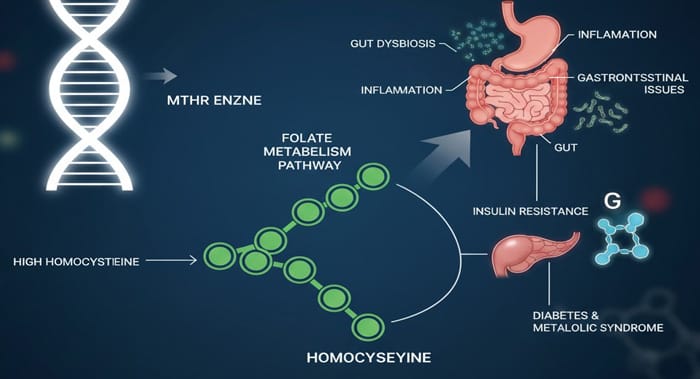
1. High levels of homocysteine have found to be a risk factor for schizophrenia. Therefore, Kevere et al (2014) wished to further examine the link between the level of homocysteine, the MTHFR C677T mutation and patients with schizophrenia. Levels of homocysteine were found to be highest in the schizophrenic group in comparison to the control group, particularly in those with the CT genotype. Overall, this study found those with increased blood homocysteine levels and the C677T mutation were at an increased risk of developing schizophrenia, especially in those with paranoid or episodic schizophrenia.
2. Lochman et al (2014) state a possible link between MTHFR C677T mutations, high homocysteine and schizophrenia. Through examining a group of schizophrenic patients, an increased risk of schizophrenia presentation was associated with MTHFR 677 CT and TT mutations when compared to healthy people. The authors also studied the relationship between C677T mutations and other polymorphisms associated with schizophrenia, and found a link with the ADRA2A polymorphism which governs the release of neurotransmitters (brain chemicals) from nerves within the brain. This study shows there could be malfunctioning occurring a genetic level with both the nervous system and methylation cycle, which is increasing the risk of schizophrenic development.