Following on from the first post in our series addressing why methylfolate is NOT necessarily the answer to a patient’s MTHFR mutation, this week we look at the B12 balance in reference to the MTR and MTRR genes.
MTR and MTRR
The MTR gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called methionine synthase. This enzyme converts homocysteine back into methionine, preventing the negative build-up of homocysteine in the blood and supplying the methionine integral for DNA methylation to occur.
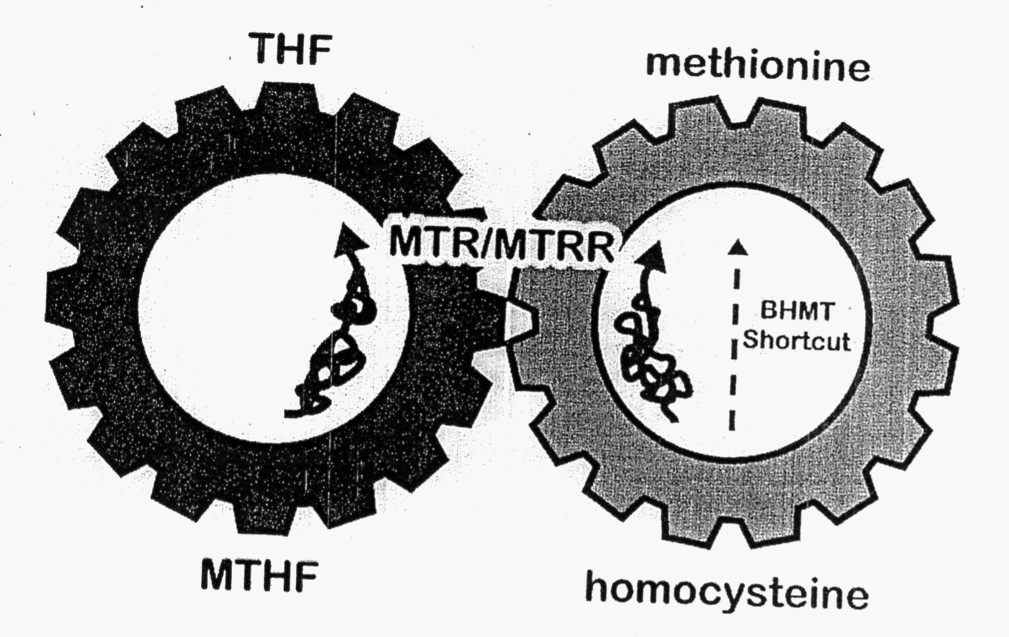
The body then uses methionine to make proteins and other important compounds, and is necessary for utilisation of methyl-groups from the folate cycle.
To function properly, methionine synthase (MTR) requires methylcobalamin (a form of vitamin B12) and another enzyme called methionine synthase reductase, which is produced from the MTRR gene.
Without methionine synthase reductase (MTRR), methionine synthase (MTR) cannot convert homocysteine to methionine. As a result, homocysteine builds up in the bloodstream, and the amount of methionine is reduced.
Therefore, if there is a mutation in the MTR or MTRR genes, they will potentially be unable to correctly synthesise methionine, which we need to utilise up the methyl-groups we create and supplement.
>>> Learn More: Introduction to the Methylation Cycles Course 1

FREE Download What is MTHFR eBook
Therefore, supplementing with methylfolate without first supporting your patients MTR and MTRR genes could do more harm than good, as their body will be unable to create the methionine needed to use the methyl-portion of their supplemented methyl-folate.
This will typically show as classic symptoms of over-methylating, as the methyl folate will be unable to be given to methionine by MTR and MTRR due to their underfunctioning.
Remember signs of over-methylation will appear as a drop in mood, aches and pains, a rash, headaches and fatigue.
We encourage you to first asses your patients RBC Folate and Serum B12 levels, as MTR and MTRR genes will have a greater initial need for methylcobalamin which is needed as as a co-factor to function. It is only once you have begun to support these mutations that the concept of methylfolate will begin to play a role.
Prevent the blocking of methylfolate within the methylation cycle by completing 23andMe genetic testing with your patients so you are able to understand the whole health picture from the outset.

- Is the world of MTHFR overwhelming?
- Lost for a concrete place to start with your patients?
To accurately prescribe methyl-folate with your patients and confidentially support MTHFR within your clinic, sign up to access our thee part webinar practitioner training series – The Foundations of MTHFR and Methylation.
>>> Learn More: Introduction to the Methylation Cycles Course 1
For all the information and to secure your place, click here or the image above.







